What is an Air-Cooled Chiller

- O que é um chiller arrefecido a ar
- O que é um refrigerador arrefecido a água
- Refrigerantes de baixo PAG em refrigeradores de semicondutores
- O que é uma câmara de combustão
- Porque é que os ensaios de circuitos integrados necessitam de refrigeradores de semicondutores
- Refrigeradores de semicondutores no teste de chips
- Resfriadores de semicondutores em Wafer Dicing
- Refrigeradores de semicondutores em embalagens
- Agosto 2025
- Julho 2025
- Junho 2025
- Maio 2025
- Março 2025
- Fevereiro 2025
- Janeiro 2025
- Dezembro 2024
- Novembro 2024
- Outubro 2024
- Setembro 2024
- Agosto 2024
- Julho 2024
- Junho 2024
- Maio 2024
- Abril 2024
- Março 2024
- Fevereiro 2024
- Setembro 2023
- Julho 2023
- Junho 2023
- Maio 2023
- Janeiro 2023
refrigerador arrefecido a ar refrigerador Instalação de chillers refrigeradores Congelador de montagem a frio refrigerador de refrigeração circulador de arrefecimento e aquecimento sistema de arrefecimento e aquecimento refrigerador de água de arrefecimento Reator de vidro de camada dupla sistema de controlo dinâmico da temperatura congelador refrigerador de refrigeração a gás circulador de aquecimento refrigerador industrial arrefecimento industrial congelador industrial frigorífico industrial reator de camisa refrigerador de refrigeração líquida refrigerador de baixa temperatura notícias refrigerador farmacêutico refrigerador de processo refrigerador do reator arrefecimento do reator arrefecimento do reator aquecimento aquecimento do reator arrefecimento sistema de reactores bomba de circulação refrigerada refrigerador de refrigeração refrigerador de parafuso refrigerador de semicondutores refrigerador de teste de semicondutores sundi tcu controlo da temperatura câmara de ensaio termóstato refrigerador de temperatura ultra baixa refrigerador de ensaio de veículos refrigerador de água refrigerador arrefecido a água wtd
Chillers are typically divided into two categories based on how they handle condensation: air-cooled chillers e water-cooled chillers. In our earlier article O que é um refrigerador arrefecido a água, we explained how those systems use cooling water to remove heat from the refrigerant. But what about air-cooled systems? How do they get the job done, and what are their advantages and limitations?
What is an Air-Cooled Chiller?
An air-cooled chiller is an industrial cooling system. The term “air-cooled” comes from the way it works—by relying on fans to blow air across the condenser to cool it down.
To make this easier to picture, think of how a household air conditioner works. The indoor unit (the evaporator) is where the refrigerant evaporates and absorbs heat, cooling the warm air inside the room.
The outdoor unit (the condenser) uses fan blades to draw in natural airflow and push it across the coils, helping release heat from the high-temperature refrigerant. Air-cooled chillers operate on the same principle, just on a larger industrial scale.

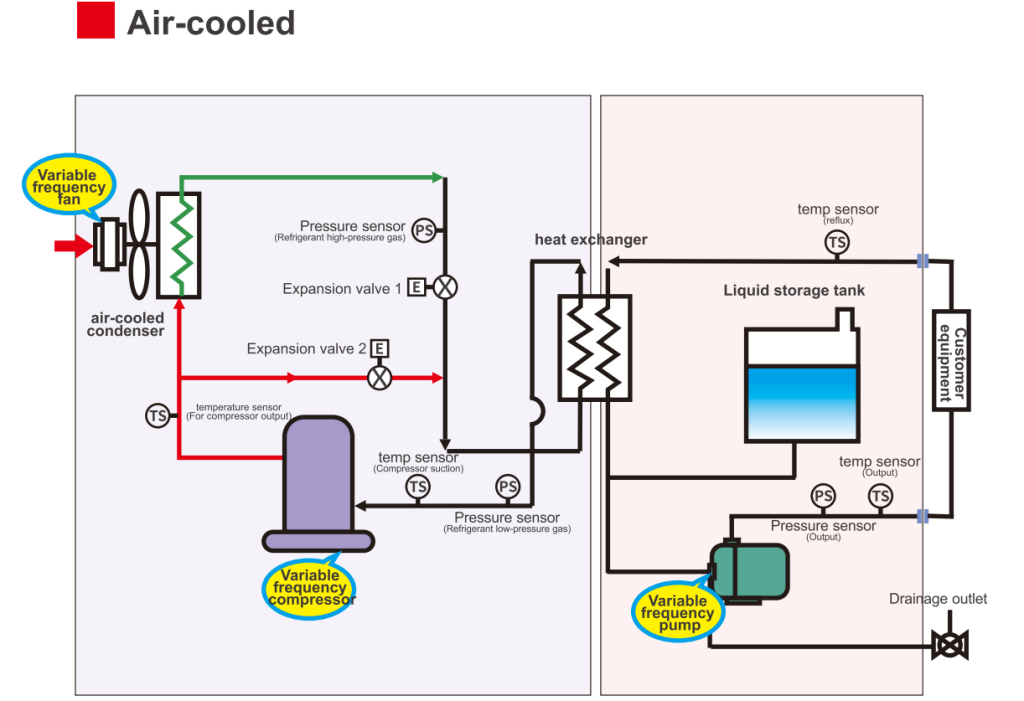
Benefits of Air-Cooled Chillers
Lower Initial Investment
Budgets often dictate equipment choices, and that’s where air-cooled systems stand out. Compared with water-cooled chillers, the initial investment is much lower. Why?
Because you don’t need complex piping or massive cooling towers—just fans at the condenser. For many small to medium-sized projects, this cost advantage makes air-cooled chillers a clear winner.
Simple Installation e Manutenção
With air-cooled chillers, there’s no need to worry about water quality or designing a complicated piping layout. You can install the unit anywhere with decent airflow. Maintenance is also straightforward and inexpensive.
Day-to-day care usually comes down to checking the fan blades and cleaning filters. Even without a specialized maintenance team, anyone with basic training can handle it.
No Water Limitations
Water-cooled chillers require reliable water sources with specific quality standards, which isn’t always practical. Air-cooled chillers, on the other hand, work entirely with air. That means no water costs, no water treatment concerns, and no worries about supply. This makes them an ideal solution in areas where water is scarce or where water quality isn’t dependable.


Limitations of Air-Cooled Chillers
Sensitive to Environmental Conditions
Compared with water-cooled chillers, air-cooled systems are much more affected by their surroundings. Because they rely on air to remove heat from the refrigerante, high outdoor temperatures can reduce heat transfer efficiency.
The system has to work harder to maintain cooling performance, which increases energy consumption—and that shows up in higher electricity bills.
Noise Levels
Large fans are essential for moving air across the condenser coils, but they come with one drawback: noise. The constant hum and buzzing of fan operation can disrupt work or living environments. In settings where quiet operation is critical, like cleanrooms or laboratories, water-cooled chillers are often the preferred choice.
Space Requirements
At first glance, it’s easy to think water-cooled systems take up more room, since they need cooling towers and piping. But if you look at the chiller unit alone, air-cooled systems are actually bulkier. They require larger fans and coils to effectively cool the refrigerant, which makes the unit itself occupy more space.
On top of that, proper installation requires open, well-ventilated areas with enough clearance for heat to escape. If you’re considering placing a chiller in a basement, stairwell, or other confined space, a water-cooled unit might be a more practical fit.
Conclusão
For small projects with limited budgets, air-cooled chillers strike a good balance between price and performance. If you’re planning a new project or thinking about upgrading an existing cooling system, LNEYA proudly offers a full range of air-cooled chillers as well as fully customized solutions.
Contact us today to learn how LNEYA can support your cooling needs.
Refrigeradores relacionados
CONTACTE-NOS
TEL:
EMAIL:
WeChat e WhatsApp:

Wechat QR

Tem alguma dúvida ou precisa de um orçamento? Preencha o formulário abaixo e a nossa equipa entrará em contacto consigo em 24 horas.
 LNEYA Refrigeradores industriais Fabricante Fornecedor
LNEYA Refrigeradores industriais Fabricante Fornecedor
















